In recent years, Medicaid spending on Long-Term Services and Supports (LTSS) has seen significant changes, reflecting broader trends in healthcare and demographic shifts. This post delves into the past and future of LTSS spending, highlighting key trends and projections.
Past Medicaid Spending on LTSS
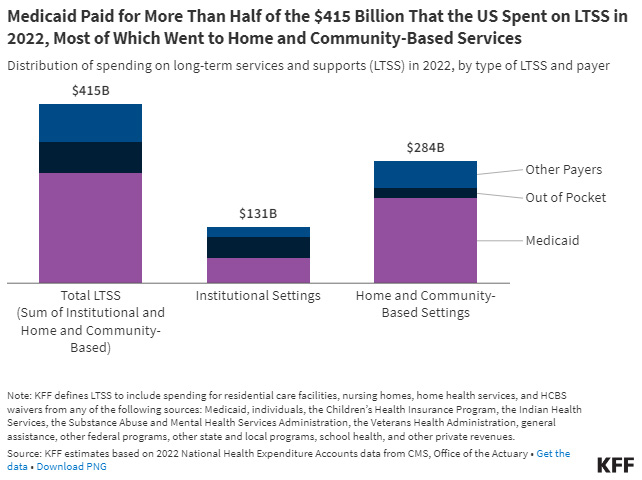
Total Spending: In 2020, Medicaid’s expenditure on LTSS reached $200.1 billion, accounting for 42.1% of all LTSS expenditures in the U.S. This substantial investment underscores Medicaid’s role as the largest single payer of LTSS in the country.
Institutional vs. Home and Community-Based Services (HCBS): Over the past three decades, there has been a notable shift towards Home and Community-Based Services (HCBS). By 2019, HCBS constituted 59% of Medicaid LTSS spending, a significant increase from just 12% in FY1989. This shift has been driven by federal incentives, such as the Deficit Reduction Act and the American Rescue Plan Act, which have encouraged states to expand HCBS offerings.
Future Spending Projections
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ (CMS) Office of the Actuary has released projections for National Health Expenditures (NHE) and health insurance enrollment for 2023-2032. Here are some key insights:
NHE Growth: The average annual growth in NHE is projected to be 5.6% over the next decade, outpacing the average annual growth in GDP (4.3%). This will increase the health spending share of GDP from 17.3% in 2022 to 19.7% in 2032.
Medicare: Medicare spending is expected to grow at an average annual rate of 7.4% from 2023 to 2032. However, this growth rate is anticipated to slow to 7.0% between 2030 and 2032 as the final wave of baby boomers enrolls in 2029.
Medicaid: Medicaid spending is projected to increase at an average annual rate of 5.2% from 2023 to 2032. The reinstatement of state eligibility redeterminations in 2023 has led to disenrollments in 2023 and 2024, but enrollment is expected to stabilize thereafter.
Demographic Shifts and LTSS Demand
The aging population in the United States will significantly increase the demand for LTSS. By 2060, the percentage of people aged 65 and older is expected to rise from 17% in 2020 to nearly 25%. Additionally, improvements to medical and assistive technologies are allowing people with intellectual /developmental disabilities to live longer. These two factors will create an increased need for LTSS over the upcoming decades.
Key Points:
Over half of people aged 65 and older will need assistance with daily activities at some point.
More than half will use paid LTSS, and over a third will require nursing home care.
An American turning 65 today will incur around $120,900 in future LTSS costs, with families covering over one-third of these costs out of pocket
Medicaid Waiver Programs
States have increasingly adopted the ACA’s streamlined eligibility renewal provisions for age and disability-related pathways, helping to retain eligible individuals in coverage and strengthen continuity of care. Thirty states now use prepopulated forms for eligibility renewals, and 43 states offer reconsideration periods for these pathways.
Currently over half of the total number of individuals on Medicaid waiver waitlists are people with I/DD.
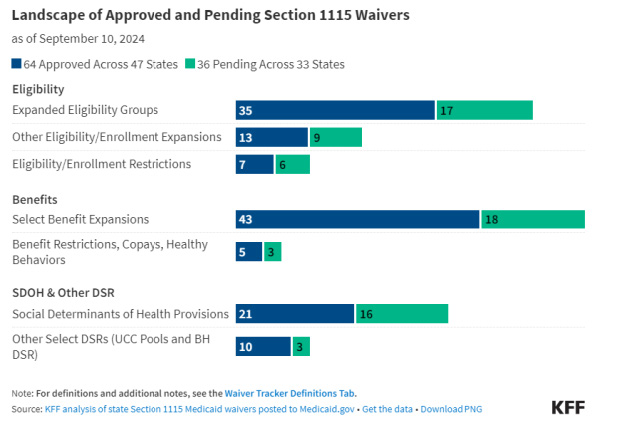
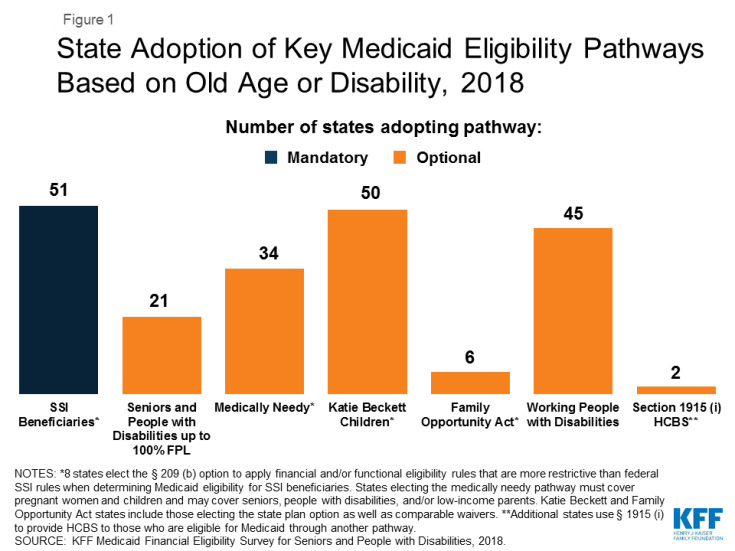
Future Eligibility and Requirements:
The future of section 1115 Medicaid waiver programs will likely be influenced by the administration elected in 2025. However, both the Trump and Harris administrations have emphasized improving access to behavioral health services.Medicaid’s role in LTSS is pivotal, with significant spending and evolving policies shaping the landscape. As the population ages and healthcare needs grow, understanding these trends and projections is crucial for stakeholders at all levels. The ongoing shift towards HCBS and the impact of federal incentives will continue to influence Medicaid’s approach to LTSS, ensuring that it meets the needs of the most vulnerable populations.
Conclusion: How CaseWorthy Can Address These Challenges
As Medicaid’s role in LTSS continues to evolve, managing the complexities of funding, eligibility, and service delivery becomes increasingly crucial. CaseWorthy’s Connect platform is designed to streamline these processes for organizations providing Medicaid-related services. With its robust case management capabilities, the platform enables efficient tracking of Medicaid waiver programs, HCBS eligibility, and client needs, ensuring that compliance with Medicaid policies is maintained. By integrating service documentation, eligibility management, and reporting in one solution, CaseWorthy allows organizations to adapt to Medicaid’s shifting priorities. As Medicaid spending on LTSS continues to grow, CaseWorthy empowers providers to better serve vulnerable populations while staying compliant with evolving regulations, ultimately improving the quality and accessibility of LTSS services.
Sources
- Congressional Research Service Report on Medicaid Coverage of Long-Term Services and Supports, September 2022
- The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services: A Year in Review June 2021 – May 2022
- KFF analysis of state Section 1115 Medicaid waivers posted to Medicaid.org, KFF.org, September 2024
- 10 Things About Long-Term Services and Supports (LTSS), KFF.org, Jul 2024
- CMS Releases 2023-2032 National Health Expenditure Projections; CMS.gov, June 2024
- What to Watch in Medicaid Section 1115 Waivers One Year into the Biden Administration; KFF.org, September 2025